AGTEAM DI ALESSANDRO GUBBINI
Body Differences
Body Differences
Couldn't load pickup availability
When it comes to fitness and body composition, there are often three main body types: endomorph, mesomorph, and ectomorph. These categories help you better understand a person's physical characteristics and how they can impact their approach to exercise and diet. Let's look at the main differences.
Endomorphic Body
Individuals with an endomorphic body type tend to have a softer, rounder body structure. Common characteristics include:
- Higher Body Fat Percentage : Endomorphs can store fat more easily than other body types.
- Robust, rounded body : Broad shoulders and broad hips are typical.
- Slower Metabolism : This body type may have difficulty losing weight.
Endomorphs often require special attention to diet and exercise to maintain a healthy body weight. Exercise programs that combine cardiovascular and strength training can be especially effective.
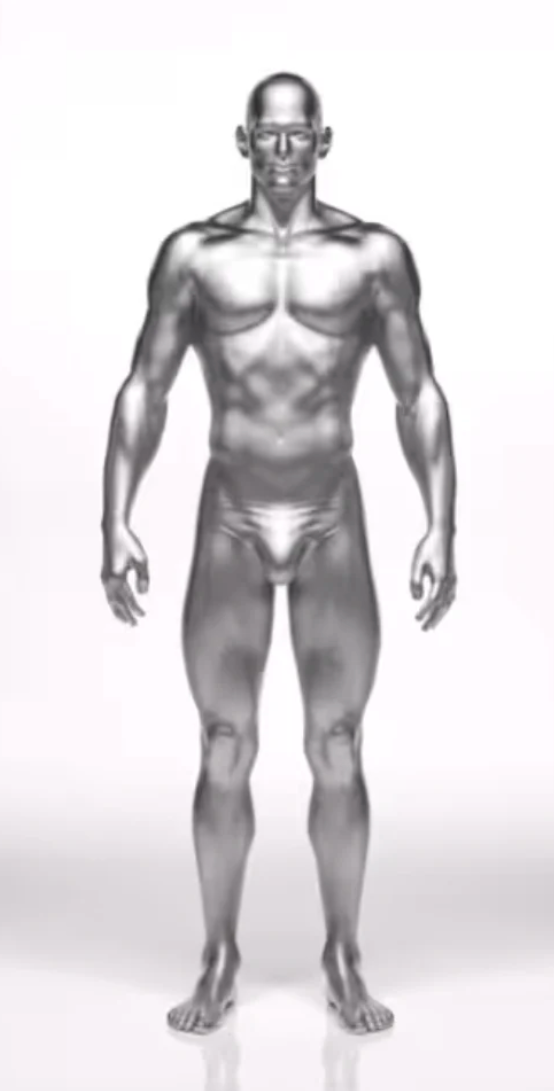
Mesomorphic Body
The mesomorph body type is often considered ideal for muscle development. Its main characteristics include:
- Athletic and Muscular Physique : Mesomorphs have a natural tendency to build muscle mass.
- Average bone structure : Broad shoulders and a narrow waist are common.
- Efficient Metabolism : They can gain muscle and lose fat with relative ease.
Mesomorphs respond well to a variety of training. They can benefit from resistance and strength training, as well as cardiovascular activities to maintain body composition.
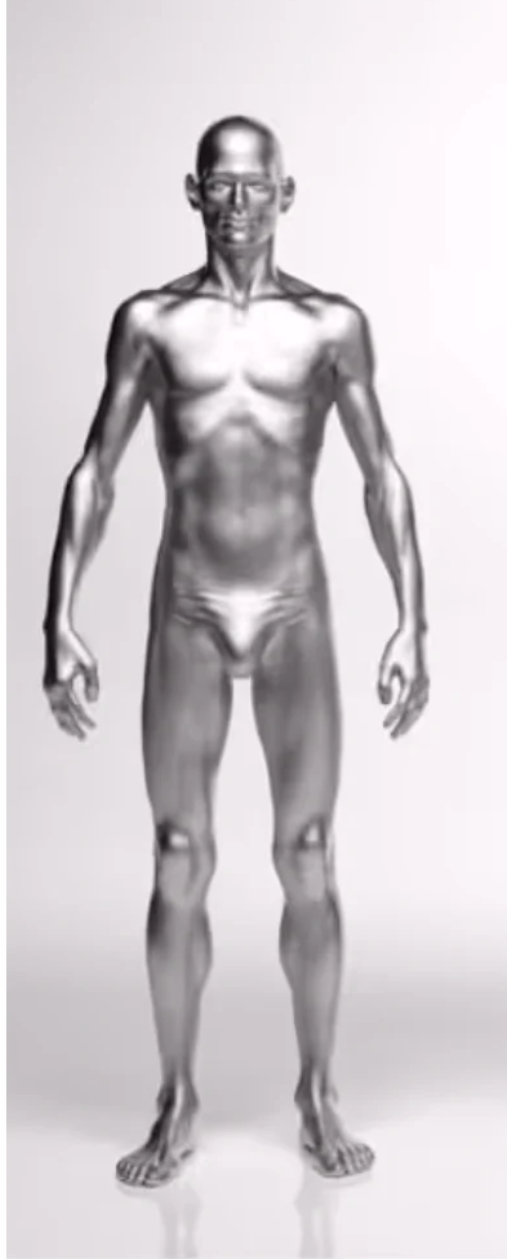
Ectomorphic Body
Ectomorphs are usually very thin and have difficulty gaining weight, whether in terms of fat or muscle. Their characteristics include:
- Slender, elongated physique : Narrow shoulders and long limbs are common.
- Low body fat percentage : They have difficulty storing fat.
- Fast Metabolism : They burn calories quickly, which can make it difficult to gain weight.
Gynoid body
The gynoid body is commonly associated with women and is characterized by:
- Fat Distribution: Body fat tends to accumulate mainly on the hips, thighs and buttocks. This distribution gives rise to the classic "pear" shape.
- Benefits: This fat distribution is often associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease than other fat distributions.
- Physical characteristics: Narrow shoulders compared to hips, well-defined waist and strong legs.
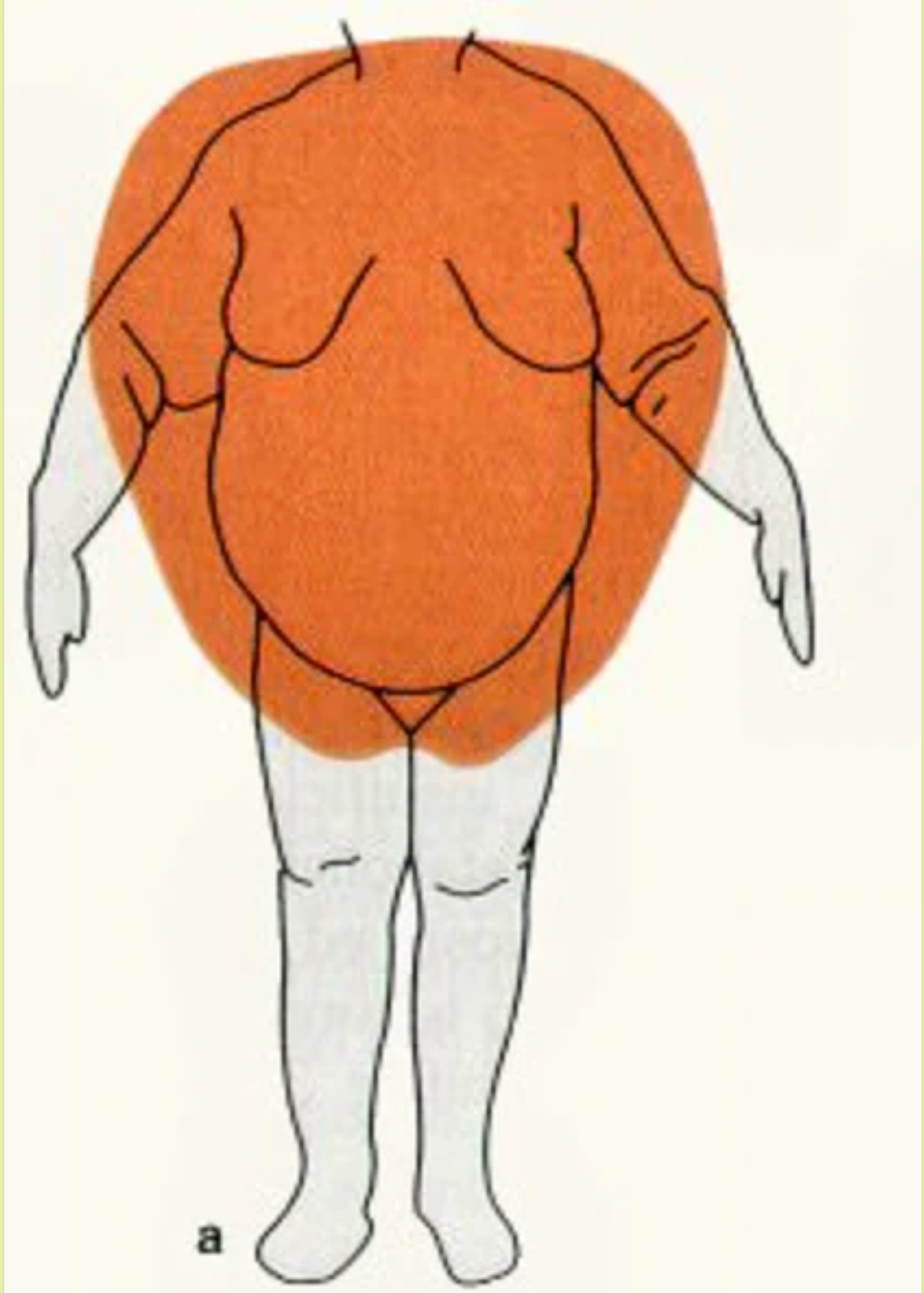
Android Body
The android body is most commonly associated with men and features the following characteristics:
- Fat Distribution: Fat is concentrated mainly in the upper body, especially on the abdomen and chest, creating an "apple" shape.
- Health Risks: This type of fat distribution is often associated with an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and hypertension.
- Physical characteristics: Broad shoulders, less defined waist and relatively thinner legs.
Share